MONiD DID Method Specification
LianXi-Tech, Dec/03/2020, V1.0.0
Abstract
The MONiD DID method aims to implement Decentralized Identifier did-core architecture in a secure, robust and flexible way. Its core technologies are built on Ethereum blockchain and the Interplanetary File System (IPFS).
Overview
The MONiD DID method uses IPFS as verifiable data registry for DID Documents. The DID Document format is like:
{
'@context': 'https://w3id.org/did/v1',
id: 'did:monid:85540cd700a8c3e37265072f2b35e3de4c3b35721e7fb02d146146262fdc8089',
publicKey: [
{
id: `did:monid:85540cd700a8c3e37265072f2b35e3de4c3b35721e7fb02d146146262fdc8089#keys-1`,
controller: 'did:monid:85540cd700a8c3e37265072f2b35e3de4c3b35721e7fb02d146146262fdc8089',
publicKeyHex: '0298a5f231fc9224ca466bdbd0b27cb34d27939d0e8aa4b65ba4ef1ed805f14975',
type: 'Secp256k1VerificationKey2018',
},
],
service: [
{
id: `did:monid:85540cd700a8c3e37265072f2b35e3de4c3b35721e7fb02d146146262fdc8089`,
type: 'MONiDPublicProfile',
serviceEndpoint: 'https://ipfs.monid.io/QmdBfKM9YQrtX5V4FvYhEVju8VsVE5488ufcJ9rWWgD892',
},
],
}
On the Ethereum side, a registry smart contract provides a mapping from a DID to an IPFS hash address of the corresponding DID Document. Given a DID, MONiD did-resolver module can retrieve the DID Document from IPFS.
Overall Architecture
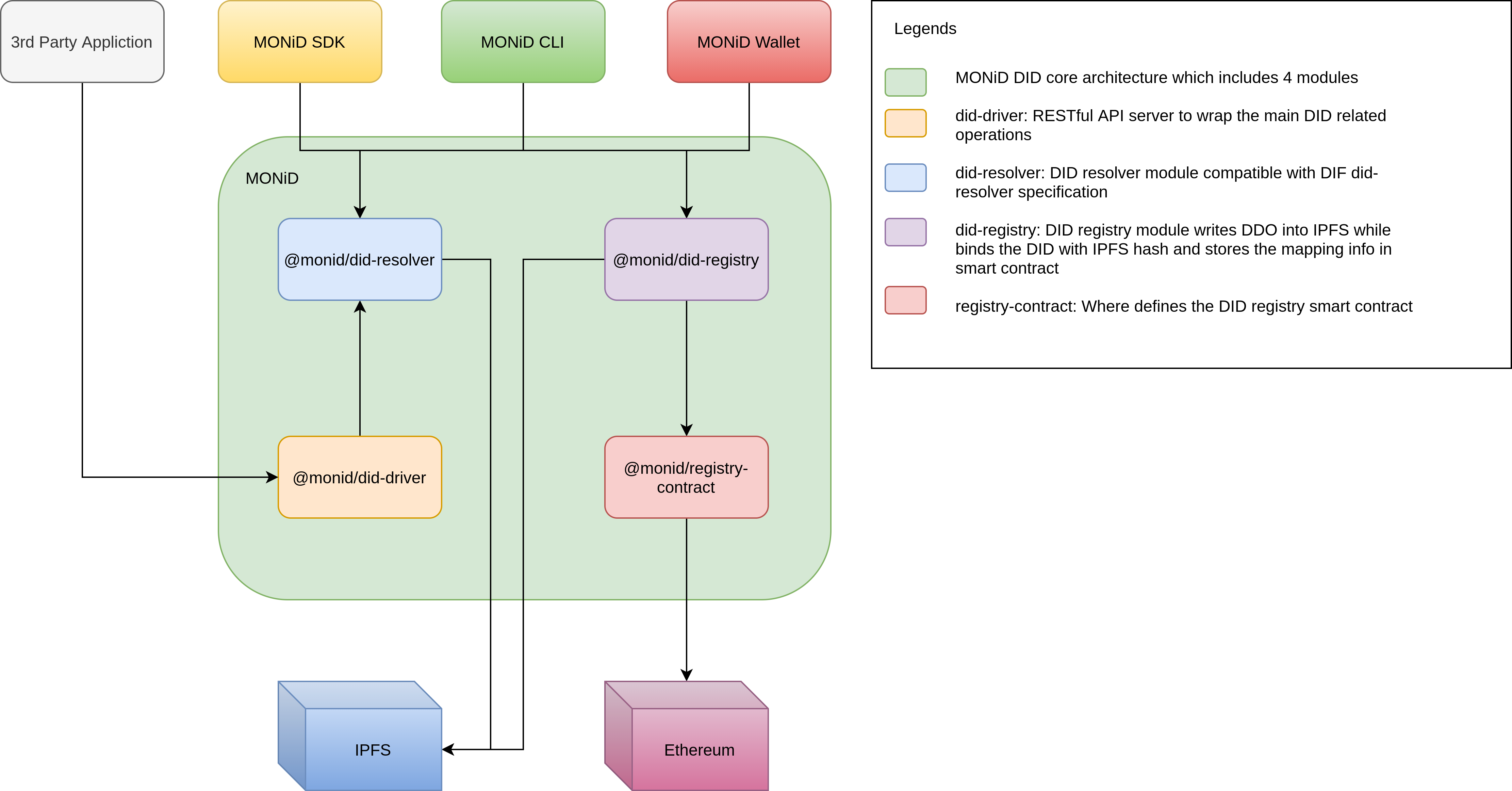
@monid/did-driver
RESTful API server to wrap the main DID operations
@monid/did-resolver
DID resolver module compatible with Decentralized Identifier did-resolver specification
@monid/did-registry
DID registry module writing DID document into IPFS and calls the registry smart contract setRecord function to map the DID with the IPFS hash address
@monid/registry-contract
Wrapper for deploying / interacting with an instance of the MONiD registry Ethereum smart contract
Specification
DID Method Format
MONiD DIDs are identifiable by did:monid: which are compatible with the W3C DID core method scheme specification
Key Management
MONiD intergrates with Torus Network, which is a decentralized key management service built on Ethereum blockchain, to provide a better user experience with high security and flexibility. A user’s private keys are splited into shares across a Torus network of nodes, and Torus allows a user to retrieve this using natural login mechanisms like social authentication. Meanwhile, Tours nodes have managed volumes and snapshot policies to ensure that key shares will never get lost.
DID Creation
There are 3 steps for MONiD to generate a new DID
- Retreives user public key from Torus Network
- Takes the keccak256 hash of the public key
- Generates MONiD DID in
did:monid:public key hashformat
DID Registration
MONiD creates the mapping from DID to IPFS address hash on the smart contract using the setRecord function, making its DID Document accessable with only the corresponding DID
DID Document Resolution
MONiD queries the registry smart contract’s getRecord function with a DID to resolve the DID document. The IPFS address can then be resolved and MONiD sends the IPFS address to MONiD IPFS Gateway to retrieve the corresponding DID Document
DID Document Updating
MONiD updates the DID document by simply using the setRecord smart contract function with the same DID and a new IPFS hash of the updated DID Document
DID Document Deactivate
Deletion is archived by updating the registry to return an all-0 byte string
Privacy and Security Considerations
Key Control
As mentioned in the Key Management section, MONiD intergrates with Torus, which provides a universal key management solution. Hence the methods for key generation, recovery and revocation are out of the MONiD architecture scope. This integration, in turn, reduces the key management risk for MONiD and its users.
MONiDPublicProfile Service Type
MONiD defines MONiDPublicProfile type in service property, just as the DID document example shows. As registered DIDs can be resolved by anyone, care must be taken to only update the registry to resolve to DID Documents which DO NOT expose any sensitive personal information.
IPFS As Verifiable Data Registry
DID Document data is immutable once it’s on IPFS. Thus no entity can change the document that a DID resolves to via the registry smart contract unless they control the private key which registered it.